1. Introduction:
The widespread adoption of cloud technology has ushered in a new era of efficiency and innovation, but it has also brought forth unprecedented challenges related to security. CloudCover refers to a holistic approach to ensure the safety of data and operations in cloud environments. This article delves into the multifaceted aspects of CloudCover, emphasizing its role in mitigating risks and bolstering the overall security posture of organizations.

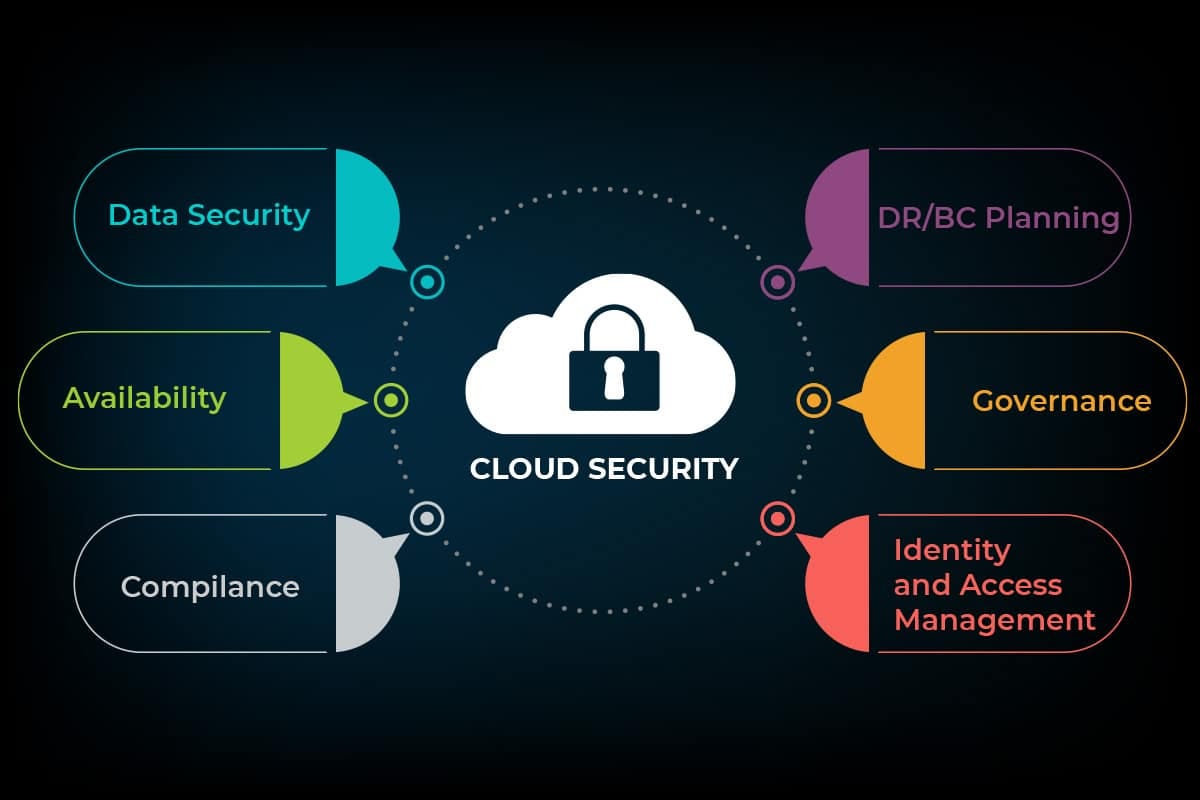
2. Understanding Cloud Security: Before delving into CloudCover, it is crucial to understand the inherent security challenges in cloud computing. Issues such as data breaches, unauthorized access, and compliance concerns are prevalent. Cloud security aims to address these challenges by implementing measures to protect data, applications, and infrastructure from potential threats.
3. Components of CloudCover: CloudCover comprises various components working in tandem to create a robust security framework. These include:
a. Data Encryption: Implementing robust encryption protocols ensures that sensitive data remains secure during transmission and storage.
b. Identity and Access Management (IAM): Effective IAM controls and monitors user access, preventing unauthorized individuals from compromising sensitive information.
c. Network Security: Securing the network infrastructure is fundamental to CloudCover, involving measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and virtual private networks (VPNs).
d. Security Audits and Monitoring: Regular audits and real-time monitoring help identify and address potential security threats promptly.
e. Compliance Management: Ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements and industry standards is crucial for maintaining a secure and compliant cloud environment.
4. The Role of Cloud Service Providers (CSPs): Cloud service providers play a pivotal role in implementing and maintaining CloudCover. Major CSPs invest heavily in security measures, offering features such as:
a. Built-In Security Protocols: Many CSPs integrate security features directly into their services, reducing the burden on users to implement additional measures.
b. Comprehensive Compliance: Leading CSPs adhere to strict compliance standards, providing users with a secure foundation to build upon.
c. Continuous Updates and Patch Management: Regular updates and patch management ensure that the cloud infrastructure remains resilient against emerging threats.
5. Challenges in Implementing CloudCover: Despite the benefits, implementing CloudCover comes with its own set of challenges. These may include:
a. Integration Complexity: Integrating diverse security measures into existing cloud infrastructures can be complex and may require careful planning.
b. User Awareness: Ensuring that users are aware of security best practices and understand their role in maintaining a secure environment is essential.
c. Emerging Threat Landscape: The evolving nature of cyber threats requires continuous adaptation of security protocols to address new challenges.
6. Future Trends in Cloud Security: Looking ahead, the field of cloud security is poised for further advancements. Future trends may include:
a. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) Integration: AI and ML technologies can enhance threat detection and response capabilities, providing a more proactive approach to security.
b. Zero Trust Security Models: The adoption of zero trust models, where no entity is inherently trusted, will likely become more widespread.
c. Quantum Computing Resilience: As quantum computing advances, ensuring the resilience of cloud security measures against quantum threats will be a focal point.
7. Conclusion: In conclusion, CloudCover is paramount in ensuring the safety of cloud technology. As organizations continue to leverage the benefits of the cloud, a proactive and comprehensive approach to security is indispensable. By understanding the components of CloudCover, the role of CSPs, and emerging trends in cloud security, businesses can fortify their cloud environments against evolving threats, safeguarding their data and operations in an ever-changing digital landscape.